| | |  | |
| | | The State Archives of Odessa Region (SAOF) is one of the largest archives in Southern Ukraine. Document holdings include more than 13,100 fonds (record groups) consisting of more than 2,009,604 files. These documents date back to the end of the eighteenth century until the present and reflect the history of the City of Odessa, Odessa Region and Southern Ukraine (formerly Novorussia). A large number of these documents are concerned with Jewish history.
The State Archives of Odessa Region was founded in 1920 as the Odessa Historical Archives. Its main function was the collection of archival documents in the territory of Odessa and Odessa Guberniya (Province), control under departmental archives, responsibility for the safety of valuable materials and the researching and publication of documents. Many famous scientists, public leaders and officials took part in the establishment of the state archival system in Odessa Region.
SAOR began with 22 fonds and collections from various organizations, agencies, religious institutions that concluded their activities after the revolution.
The main fonds of the pre-revolutionary period were:
|
|
| • Administration of Novorussia and Bessarabia Governor-General
• Odessa City Chief
• Odessa City Council
• Guardianship Committee for Foreign Settlers in Southern Russia
• Odessa Police Office
• Commercial Court
• Banks
• Odessa Port Offices and Customs
• Novorussijsky University, colleges and schools
• Building organizations
• Cultural Societies
|
Jewish materials were represented as separate parts of those finds (Jewish sections) or in common management records.
From the mid 1920s until 1940, the Odessa Archive received 33 fonds from Jewish institutions, including:
|
|
| • Odessa Affiliate of the Committee of Society for the Spreading of
Learning Among the Jews in Russia
• Private Banks of Ashkenazi and Barbash
• Odessa City Rabbi
|
|
|
| 
| 1901 Marriage record of
Zalman Zavelsky (age 30,
son of Aron, from Glukhov)
and Machla Feiga Khazanov
(age 19, daughter of Israel-
Ber, from Sosnitsa)
Source: Fond 39, Opis 5,
Delo 100, Page 153,
Document #205
[Enlarge image] |
|
|
| • Talmud Torah
• College for Artisans of Society “Trud” (Labor”), KOMZET, ORTVERBAND
• Odessa Pedagogical Jewish College
|
These fonds were of great interest to researchers. During this time, there was open support and acceptance of various ethnic groups. In 1931, the Jewish section in the Odessa Archives was established; the Search Room opened in 1927 and scientists received extensive access to documents. The first Odessa historians working with Jewish records were:
|
|
| • S. Borovoj (“Jewish Colonies in Novorussia, 1830-1840”)
• L. Strizhak (“Economic state of the Jews in the Steppe Ukraine”)
• A. Buzhevich (Jewish Commissions, 1882”)
• D. Rishman (“History of Jews in Novorussia”)
• A. Reminik (“Jewish Theatre”
|
The academician, M. Slabchenko, prepared the materials of Zhaporozje Sich Kosh for publication and located Jewish records among them; but the research and qualified description of them was made by the a young scientist, Saul Borovoj. In 1940, S., Borovoj defended a doctoral dissertation on the subject of “Studying the History of Jews in Ukraine, XVI-XVIII centuries.”
With the beginning of World War II and German-Romanian occupation of Odessa in 1941, a major portion of the documents were evacuated to Stalingrad and later to the town of Uralsk in the West Kazakhstan Region. In Odessa, the City Chief Alexianu ordered the liquidation of “all Soviet garbage” and to convert the archives into a horse stable. The Director of the Archives, G. Serbsky, did not obey and valuable documents were salvaged. Replacements and evacuations led to irrecoverable waste; more than one million files (50% were lost during the war. Jewish fonds also suffered very much. For example, documents destroyed included great portions of materials of:
|
|
| • Odessa City Rabbi (320-819 files)
• Odessa Affiliate of the Committee of Society of the Spread of
Learning Amount the Jews in Russia (462-495 files)
• Odessa House of Jewish
• Culture (82-84 files, and others
|
In April 1944, SAOR renewed its work in Odessa. After the war, there were not significant incoming Jewish materials other than some private fonds. Since 1990, SAOR has begun the process of declassifying about 900 fonds of German-Romanian Occupying Administrative and other Institutions. These files contain information about the creation of 139 concentration camps and ghettos in”Transnistra,” names of the imprisoned Jews and the policy of genocide.
In 1992, SAOR included records of the former Archives of Odessa Regional Committee of the Communist Party of the USSR (more than 6,000 fonds), including Jewish fonds such as:
|
|
| • Odessa Region and City Committees of Poalei-Zion
• Odessa Region Committee of Jewish Communist Union of Youth
• Editorial Office of the newspaper “Kommunistische Stimme” and others.
|
From 1945 until the early 1990s, scientists did not conduct special research on Jewish history. In spite of the fact that Jewish fonds were not secret, there was not any information about them in the Guide to Odessa Archives published in 1961.
Interest in this subject developed from the beginning of the 1990s. During the last 13 years, fifteen foreign researchers, representing scientific center in Germany, Israel, USA, Canada and Japan as well as Ukrainian historians and others have made great contributions to Jewish history using extensive archival sources.
The historical focus on national minorities in Novorussia is one of the main directions of activity in the Odessa Archives in recent years. Materials on Jewish history were presented at some exhibits at the Odessa Historical and Literary Museums. In 2000, the complete register of fonds and collections, including Jewish ones, for pre-revolution period was published, Also, some databases were created including:
|
|
| • Name Indexes of the Odessa Jews on Materials of the First All-Russian
Census in 1897 (not complete)
• Odessa Board for Small Businesses, 1894-1918
|
The name and thematic catalogs of Jews were also brought up to date. SAOR participates in the international program “Documents on History and Culture of Jews in Archives of Ukraine” (Ukraine-Russia-USA).
One of the recent projects of the Odessa Archives is an archeographical edition of Jews of Odessa and Southern Ukraine: History in Documents (End of XVIII-Beginning of XX Century). The book was prepared with support from the Odessa department of the “Joint” and was published in 2003. The book includes:
| 1 |
| Survey of 72 basic fonds of the Odessa Archives for pre-revolutionary and Soviet periods which contain documents on Jewish history (33 fonds of Jewish institutions, 24 fonds of administrative, court, statistics, customs and other institutions that were related to the subject and 15 private fonds). Description of every fond provides information about inclusive dates and quantity of files, varieties and contents of documents in general.
| | 2 | | Documental Digest. 250 documents on pre-revolutionary history of Jews are represented on 12 thematical lines including:
|
|
|
| • Legislation on Jews, State policy and the Jewish subject in the
Russian Empire
• Settlement in Novorussia, Jewish colonies, migration and emigration
• Trade, industry, banks
• Educational movements; science
• Religious and moral life
• Charity
• Medical institutions and societies
• Publishing business
• Jewish pogroms
• Army service
• Participation in revolution movements
• Criminal world
Document examples
• Regulation for Jews (April 13, 1835)
• Directions of Higher Authorities about the foundation of the Commission
for Education of Jews (1842)
• Abolition of kahals (1844)
• Settlement of Jews on State lands (1847)
• Prohibition of special Jewish clothes (1851)
• Visits to police office on day off (1852)
• Election order for Jews (1857)
• Registration Rules for Jews – foreign subjects (1880)
• Materials of the Commission on the Jewish Problem (1881)
• Directions regarding admission of Jews to universities (1913)
• Circular of the Ministry of Jewish Affairs regarding election to Jewish
public boards (1818)
• Information about resettling Jews from Podolia to Kherson Guberniyas
and the number of Jewish colonies (1835-1839)
• Project of some merchants from Kremenchug, Pavlograd and Uman
to establish a model Jewish colony of Michailsdorf in Bessarabia (1840)
• Report of the Governor-General M.S. Vorontsov regarding reformation
of the Jews in Russia (1844)
• Appointment of the Mennonite Quenzer to the post of Chief in the
colony of Gromokleva (1857)
• Conflict and fighting between the Jews and Gypsies in Rezina
(Bessarabia)
• Activities of the Odessa Society for Relief to Jews, Peasants and
Artisans in Syria and Palestine (1888)
• Jewish Colonization Society (1892)
• Emigration from Odessa to Argentina (1895)
• Inclusion of Jews to the Odessa merchants and petty bourgeois
• Foundation of A. Rafalovich’s firm (1850)
• Society for Bilateral Aid to Jewish counterman (manager) (1862)
• Registration of owners of manufacturing enterprises in Odessa (1898)
• Information about activities of the M. Ashkenazi firm (1898)
• S. Barbash’s bank (1915)
• Materials about the Foundation of the Jewish College for Boys in
Odessa (1826)
• Odessa Jewish Society “Beseda” (Converse”) (1863)
• Society for Bilaterial Aid to the Jewish teachers in Novorussia (1866)
• Activities of the Talmud Tora in Odessa (1877)
• Statistical information about Jewish students in the Novorussijsky
University (1881)
• Establishing of S. Gurovich and R. Khari scholarships at Odessa Commercial College (1888, 1892)
• Activities of the Society “Trud” (1895-1901)
• Odessa Affiliate of the Committee of Society of the Spread of Learning
among Jews in Russia (1897)
• Cheders in Ekaterinoslav and Tavrich Provinces (1903)
• Building of the Second Talmud Torah in Odessa (1904)
• Activities of Societies of “Ivrija” (1907)
• Lovers of Jewish Language (1907)
• Club “The Jewish Public Meeting” (1908)
• Odessa Jewish Public Nachman Byalik Library “Seifer” (1919)
• The College “Yeshivot” (1915-1916)
• Documents about the number of synagogues and houses of prayer
in Odessa (1840)
• Commendation to the Rabbi of the colonies of Novo-Vitebsk, Novo-
Podolsk and Novo-Kovno – Rabbi Benjamin Knyazhik with gold medal
for good service (1862)
• Registration of 63 synagogues and houses of prayer in Odessa with
dates of foundation and addresses (1890-1894)
• Materials about parishioners of the Brodsky Synagogue (1892-1894)
• Statute of the Odessa Society for Jews Converted to the (Russian)
Orthodox Faith (1894
• Birth entry of David Oustrach (1908)
• Information about the Jewish Hospital in Odessa (1832,1854)
• Establishing of the Iosif Valtuch Orthopedic Institute (1888)
• Klara Weinberg’s Medical Center for Vaccination against smallpox
(1893)
• Documents about prohibition of the merchant Aksenfeld to open a
printing house in Odessa (1852)
• Program of the first magazine for Jews in Russian “Rassvet” (*1860)
• Information about edition of “Hamelitz (1867)
• “Kadima” (1906)
• “Unser Leben” (1912)
• “Jewish Anecdotes” (1916
• Materials from the editorial collection of Sergey Stern
• Materials about the establishment of:
• Odessa Jewish Charity Society (1866)
• Kogan’s House (1873)
• Jewish Hospice (1880)
• Benefections of A. Brodsky, R. Khari, OKhais, M. Morgulis, M.
Rabinovich, Rafalovich, Katzen, Luisa Ashkenazi and others for
Jewish orphans (1866-1898)
• Activities of the Societies of “Druzhelyubije” [“Friendship”] (1898)
• Central Jewish Registration Bureau
• Reports and notes of the extraordinary Odessa Governor-General,
gubernial authorities and Odessa City Chief about pogroms in Odessa
and Novorussia in 1881, 1886, 1905
• Evidence from witnesses including Rosa Drutman’s statement about
the murder of the Veitzman family in 1905.
• Information about the liberation of Jewish students from military
service (1844)
• Drafting of Jewish peasants who were avoiding military service (1847)
• Materials about legal proceedings charging E. Kenis with abetting Jews
in avoiding military service (1885-1888).
• Materials from the police court case of David Bronstein (Lev Trotsky)
arrested for revolutionary activities in Nikolayev (1898)
• Reports of police officers about participation of Jews in revolutionary
developments, court materials accusing M. Bogomolny with having
illegal Bund and Poalei-Zion literature (1904)
• Activities of the Jewish Self-Defense guard in Moldavanka
[Odessa] (1906)
• Relationship of cadets (political party) to the “Jewish Problem” (1908)
• Reports of Police and Customs authorities about the Jews engaged in
contraband, forgery, prostitution (international), discreditable
practices with securities, etc.
|
| 3 |
| Genealogical Chapter, Fond 359: Odessa Board for Small Business, Jewish Section, 1894-1918 (alphabetical name index of 4,505 heads of Jewish families that had a status of Odessa Meshchanin (petty bourgeois) with address locations.
| |
|
| 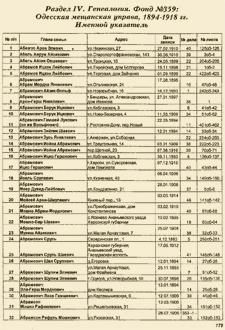
| Page 179 from the above book
with an alphabetical name index
of 4,505 heads of Jewish families.
Information includes name,
address, date of birth,
age and list number.
[Enlarge image] |
Genealogical research is a way to examine the facts through the history of families and to determine the place of an individual in society and his influence on the world. This is an important research focus in order to understand the historical period, its affect on individual families and our place in history.
For example, family history research for the Odessa petty bourgeois Krakhmalnikovs revealed an engrossing story of the development of confectionary production that began in 1892 as a factory and trade firm “The Krakhmalnikov Brothers” and continues to operate now as the Joint Stock Company “Odessa.” By the way, descendants of this family now live in the USA after emigrating from Odessa in 1906. Some family members continue in this occupational field including Bruce Kreig, a grandson of Abram Krakhmalnikov. While he is a professor of Archeology at Chicago University, at the same time he is a famous international expert in food and cooking. After searching the documentary materials in the Odessa Archives, he wrote “We are very happy to know that we are a part of the history of Odessa.”
|
|
| BIOGRAPHY
Lilia Belousova, is a graduate of Odessa State University, Department of History. She has worked for the Odessa Oblast Archives for twenty years and is currently the Vice-Director of this Archive. She has participated in numerous international conferences as a lecturer. One of her specialities is Jewish genealogical research and she is the author of The Jews of Odessa and Southern Ukraine: The History in Documents (end of XVIII-Beginning of XX Century) published in Odessa in 2002, jointly by the Archives and “Migdal” (Jewish Community in Odessa). Lilia enjoys cooking and her article entitled “Cuisine and Cooking Traditions of Odessa was published in 2000 in “Wostock”, a journal published in Germany. She is Editor of the annual series of archival guides dating from 2000. She works closely with the local Jewish community on various projects.
back to top
| | | << RTR Foundation Home Page | | |